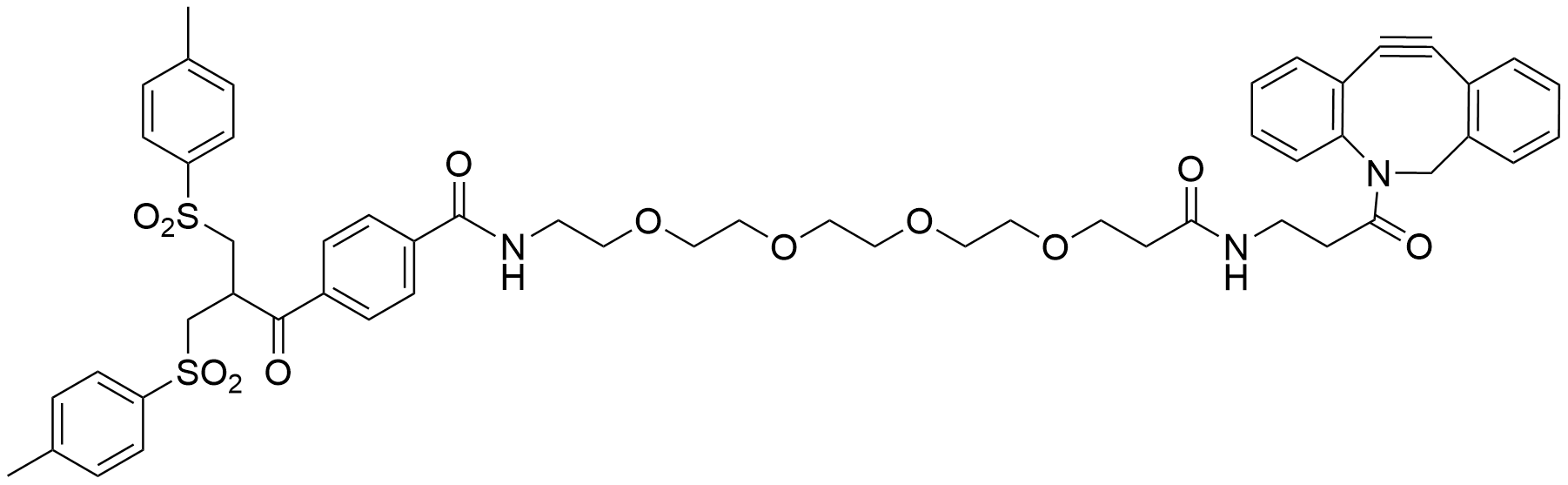
Bis-sulfone-PEG4-DBCO
Bis-sulfone-PEG4-DBCO is a bis-alkylating labeling reagent that enables site-specific incorporation of DBCO moiety onto antibodies to form well-defined conjugates. This approach involves two steps: (1) disulfide reduction to release the two cysteine thiols and (2) re-forming the disulfide by bis-alkylation via a three-carbon bridge to which DBCO moiety is covalently attached. During this process, irreversible denaturation of the protein, disrupting either their tertiary structure or their biological activity does not occur.
The covalent, site-specific conjugation of PEG to a polyhistidine tag (His-tag) on a protein with bis-alkylating reagents was also reported in literature (see Selected References section).
1.Khalili, H., et al. (2012). Comparative Binding of Disulfide-Bridged PEG-Fabs. Bioconjug. Chem., 23(11), 2262-77. [PubMed]
2.Badescu, G., et al. (2014). Bridging Disulfides for Stable and Defined Antibody Drug Conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem., 25(6), 1124-36. [PubMed]
3.Brocchini, S., et al. (2008). Disulfide bridge based PEGylation of proteins. Adv Drug Deliv Rev., 60, 3-12. [PubMed]
4.Balan, S., et al. (2007). Site-Specific PEGylation of Protein Disulfide Bonds Using a Three-Carbon Bridge. Bioconjugate Chem.,, 18, 61-76. [PubMed]
5.Wang, T., et al. (2014). Bis-sulfide bioconjugates for glutathione triggered tumor responsive drug release. ChemComm.,, 50, 1116-1118. [PubMed]
6.Wilbur, T., et al. (1994). Monoclonal antibody Fab’ fragment cross-linking using equilibrium transfer alkylation reagents. A strategy for site-specific conjugation of diagnostic and therapeutic agents with F(ab’)2 fragments. Bioconjugate Chem.,, 5, 220-235. [PubMed]
Site specific conjugation to a polyhistidine tag (His-tag).
7.Cong, Y., et al. (2012). Site-Specific PEGylation at Histidine Tags. Bioconjugate Chem.,, 23, 148-263. [PubMed]
Abs/Em Maxima: 346/445 nmExtinction Coefficient: 19,000Spectrally Similar Dyes: Alexa Fluor? 350, CF? 350, DyLight 350, AMCAAZDye? 350 is a blue-fluorescent azide-activated probe that reacts with terminal alkynes via a copper-catalyzed click react…
Abs/Em Maxima: 402/424 nmExtinction Coefficient: 35,000Flow Cytometry Laser Line: 405 nmMicroscopy Laser Line: 405 nmSpectrally Similar Dyes: Alexa Fluor? 405, CF? 405, Cascade Blue?, DyLight? 405AZDye? 405 Azide is a water-soluble, pH-insensiti…
Abs/Em Maxima: 346/445 nmExtinction Coefficient: 19,000Spectrally Similar Dyes: Alexa Fluor? 350, CF? 350, DyLight 350, AMCAAZDye? 350 Alkyne (Alexa Fluor? 350 Alkyne equivalent) is a blue-fluorescent, alkyne-activated probe that reacts with azid…
Abs/Em Maxima: 430/537 nmExtinction Coefficient: 15,000Spectrally Similar Dyes: Alexa Fluor? 430, CF? 430AZDye? 430 Azide is a water-soluble, green-fluorescent azide-activated probe that reacts with terminal alkynes via a copper-catalyzed click re…
Abs/Em Maxima: 346/445 nmExtinction Coefficient: 19,000Spectrally Similar Dyes: Alexa Fluor? 350, CF? 350, DyLight 350, AMCAAZDye? 350 DBCO reacts with azides via a copper-free “click chemistry” reaction to form a stable triazole and does not re…
Abs/Em Maxima: 402/424 nmExtinction Coefficient: 35,000Flow Cytometry Laser Line: 405 nmMicroscopy Laser Line: 405 nmSpectrally Similar Dyes: Alexa Fluor? 405, CF? 405, Cascade Blue?, DyLight? 405AZDye? 405 Alkyne reacts with azides via a copper…
Abs/Em Maxima: 494/517 nmExtinction Coefficient: 73.000Flow Cytometry Laser Line: 488 nmMicroscopy Laser Line: 488 nmSpectrally Similar Dyes: Fluorescein, Alexa Fluor? 488, CF? 488A, DyLight? 488, Atto? 488AZDye? 488 Azide (Alexa Fluor? 488 Azi…
Abs/Em Maxima: 402/424 nmExtinction Coefficient: 35,000Flow Cytometry Laser Line: 405 nmMicroscopy Laser Line: 405 nmSpectrally Similar Dyes: Alexa Fluor? 405, CF? 405, Cascade Blue?, DyLight? 405ZDye? 405 DBCO reacts with azides via a copper-fr…
